Testing Hypotheses σ is known and n > 30 I One sample test for the population mean 1 H0 µ=µo 2 Ha µ≠µo;The choice of n = 30 for a boundary between small and large samples is a rule of thumb, only There is a large number of books that quote (around) this value, for example, Hogg and Tanis' Probability and Statistical Inference (7e) says "greater than 25 or 30" (n=30) Nonanemic in Infancy (n=133) Gross Motor Score Verbal IQ `

Comparison Of Means One Sample Unknown Population Sd Env710 Statistics Review Website
N 30 statistical significance
N 30 statistical significance-30 Figure 2 Repair times for Verizon data set;The probability that the sample mean age is more than 30 is given by P (X ¯ > 30) P (X ¯ > 30) = normalcdf(30,E99,34,15) = Let k = the 95 th percentile k = invNorm ( 0 95,34, 15 100 ) ( 0 95,34, 15 100 ) = 365




Summary Hypothesis Testing Selfengagement Assesment Null Hypothesis Song
If we take a random sample size of 30 bills, the smallest nonzero defect we can detect would be a single error This translates into 1/30 = 033 for a defect rate of 33%ILEC and CLEC groups (n = 1664 and n = 23, respectively) Data are in the top panels, and bootstrap distributions for the mean of each group at bottom 23 Bushmeat Regression Example Brashares et al (04) discuss the relationship between fish supply and the loss of wildlife due to bushmeat huntingIn statistical analysis, the rule of three states that if a certain event did not occur in a sample with n subjects, the interval from 0 to 3/ n is a 95% confidence interval for the rate of occurrences in the populationWhen n is greater than 30, this is a good approximation of results from more sensitive tests For example, a painrelief drug is tested on 1500 human subjects, and no adverse
But you can use the standard deviation of your sample if you have enough observations at least n=30The answer is that in "Intro to Statistics" classes, they give a rule of thumb that, for "nice" distributions, n = 30 is large enough that claiming the sample mean is approximately normally distributed is probably not that far off the truth if you know the population standard deviation, and this is justified because of the asymptotic behavior of sample means (they are asymptoticallyWhat's the meaning og n>30 in statistics?
With n ≥ 30, the difference between the value of t and the value of Z is less than 5%, acceptable from a practical point of view Previous post Optimization of Pharmaceutical Production Processes through LeanSigmaIt means that the sample size, n, is greater than 30 This is a crude rule of thumb that suggest that the normal distribution could be a reasonable approximation if you want to make inferences about the mean It isGiven , n = 25 ( small, n< 30 so use tstatistics), s = 30 and since, Step 1 Hypothesis The claim that or 170 = 160, the null hypothesis Since xbar is smaller than , the alternate hypothesis is 170 > 160 H 0 = 160 H a Step 2 Select level of significance This is given as (5%) Step 3 Test statistics and observed value Step 4




Statistics Tutor New York Private Stats Lessons In Ny Econtutor




New Curriculum 08 Department Of Statistics Statistical Inference
Relying on the Central Limit Theorem, various references state that a minimum sample size of 30 (you may also see or 25, but we'll assume 30 here) is necessary for the distribution of $\bar{X}$ to be close enough to a Normal distribution, which you refer to here as the "Rule of 30" If the number of samples you collect is at least 30, it's reasonable to assume that $\bar{X}$ follows a 4 Testing Normality Using SPSS We consider two examples from previously published data serum magnesium levels in 12–16 year old girls (with normal distribution, n = 30) and serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in adult control subjects (with nonnormal distribution, n = 24) ()SPSS provides the KS (with Lilliefors correction) and the ShapiroWilkIndeed the convergence rate of T(n) to N(0,1) is O(n^1/2) so again at n=30 you are likely past the point of diminishing returns and would expect only small variations and so N(0,1) is a reliable
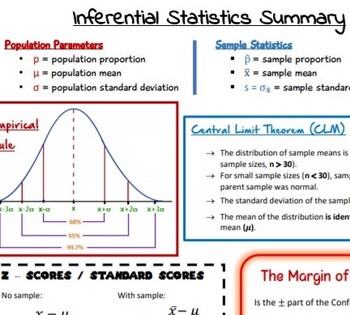



Inferential Statistics Summary By Niamh O Shea Tpt



1
T distribution is the distribution of any random variable 't' Below given is the T table for you to refer the one and two tailed t distribution with ease It can be used when the population standard deviation (σ) is not known and the sample size is small (n30)µµo 3 Test statistic Assume that H0 is true and see if you have enough data/evidence to reject it 3B How far sample mean x is from µ n x z o σ −µ = 4Caution you should really use the standard deviation of the entire population!




Statistical Distributions 34 638 Samantha Mitchell Dix
.jpg)



Statext Statistical Probability Tables
The usual guideline, which is usually taught by people who have no formal training in statistics, is that a sample size of 30 is large enough that the sample mean has "converged" to normal Whether or not that's true depends on the distribution and what kind of error you're willing to tolerate




Stimulating Statistics Simulations News From The Nest




Please Help Find Test Statistic And P Value Math 1 Intro To Prob And Statistics Mowe Homeworklib



Why Is Normal Distribution Important In Statistics Quora




Finding Complete Sufficient Statistic Cross Validated




Sta 296 Exam 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Standard Errors Of Some Statistics




Statistics For Management May 30 16 Chandrasekaran N And Umaparvathi M Chandrasekaran Umaparvathi Amazon Com Books




Faq How To Calculate Power Using Simulation Stata
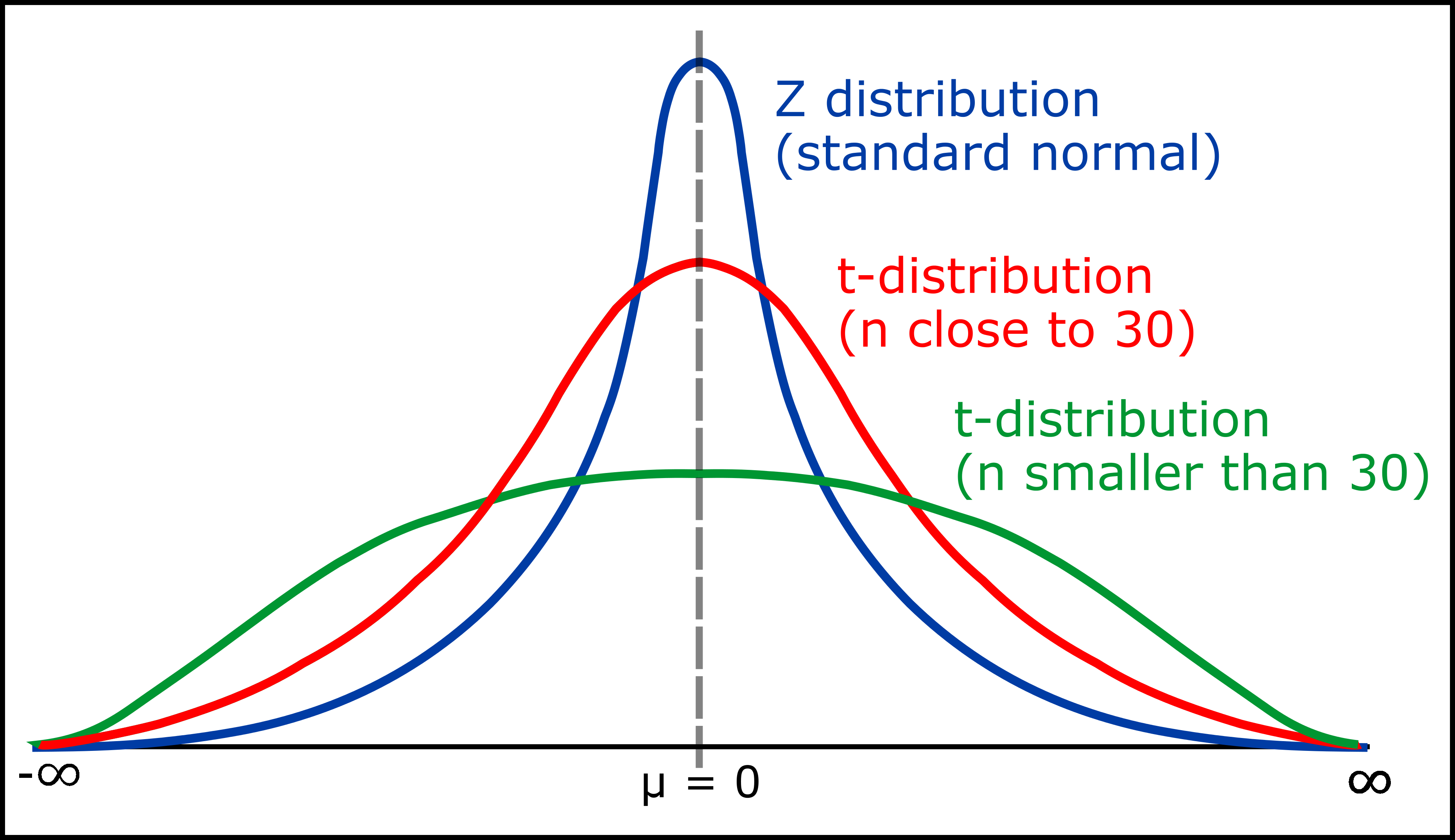



Student S T Distribution In Statistics Geeksforgeeks



Plos One Characterization Of Near Death Experiences Using Text Mining Analyses A Preliminary Study




Intro To Statistics Part 11 Statistical Significance And Null Hypothesis Testing L0ng C0nnect10ns




25 Best Memes About Central Limit Theorem Central Limit Theorem Memes




You Can T Assume A Normal Distribution For Your Data With N 30



2




Inferential Statistics Population Curve Mean Mean Group Of Ppt Download




Faq How To Calculate Power Using Simulation Stata




Solved Hypotheses Test For Two Samples Two Samples Are Chegg Com




Glen Koskela Is Unsubscribe The Worst Cx Before Summer Vacation I Tend To Opt Out From Many Newsletters All Well Known Sources I Kept Statistics Of It N 30 I Ignored




Descriptive Statistics Of Contact Indices N 30 2 Hour Observation Time Download Scientific Diagram




The Sampling Distribution Of The Sample Mean




Descriptive Statistics N 30 Download Table




Answered The Population Of Current Statistics Bartleby
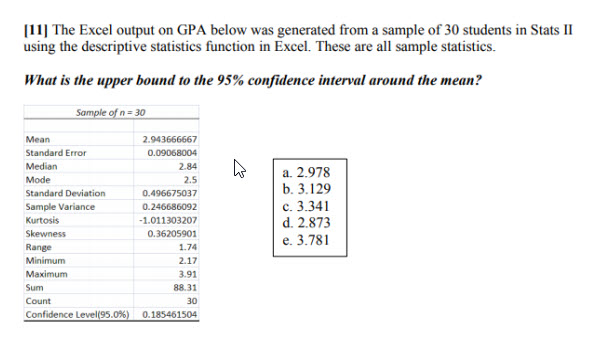



Solved 11 The Excel Output On Gpa Below Was Generated From Chegg Com




T Distributions And Tests




Chapter 5 Normal Probability Distributions N Elementary Statistics




Sampling Distribution Of Large Sample Mean Shs Statistics And Probability Q3 Youtube




Descriptive Statistics Of Physical Chemical Soil Variables N 30 Download Scientific Diagram
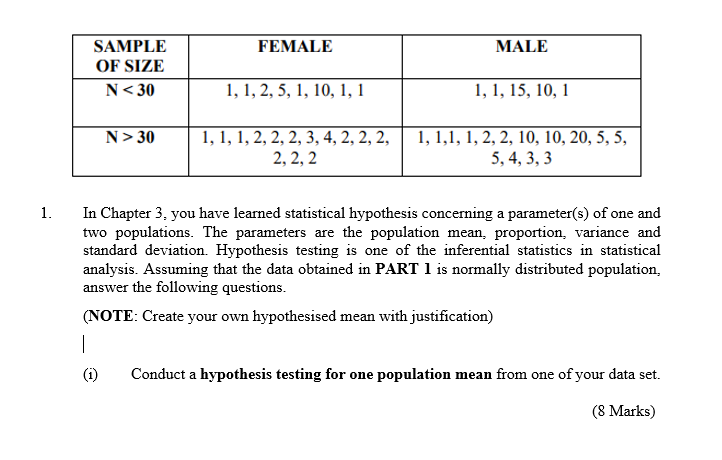



Solved Female Male Sample Of Size N 30 1 1 2 5 1 10 1 Chegg Com




Pdf Is The N 30 Rule Of Thumb Of Ecological Field Studies Reliable A Call For Greater Attention To The Variability In Our Data



Solved Worksheet 1 Descriptive Statistics N 1 N 5 N 10 N 30 N 100 Statistics Variable N N Mean Se Mean Stdev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Maximum N 1 Course Hero



Why Is N 30 Considered A Large Sample In Statistics Statistics




T Distributions And Tests




A Comparison Of Some Test Statistics For Multivariate Analysis Of Variance Model With Non Normal Responses Semantic Scholar




What Is The Rationale Behind The Magic Number 30 In Statistics




Solved In A Certain Binomial Distribution 0 And N 30 In Using The Normal Approximation A What



1




Don T Teach Statistics In High School Dovydas Joksas




Chapter 7 Hypothesis Testing With One Sample 7



1




For Dummies Statistics Math Math Methods Statistics
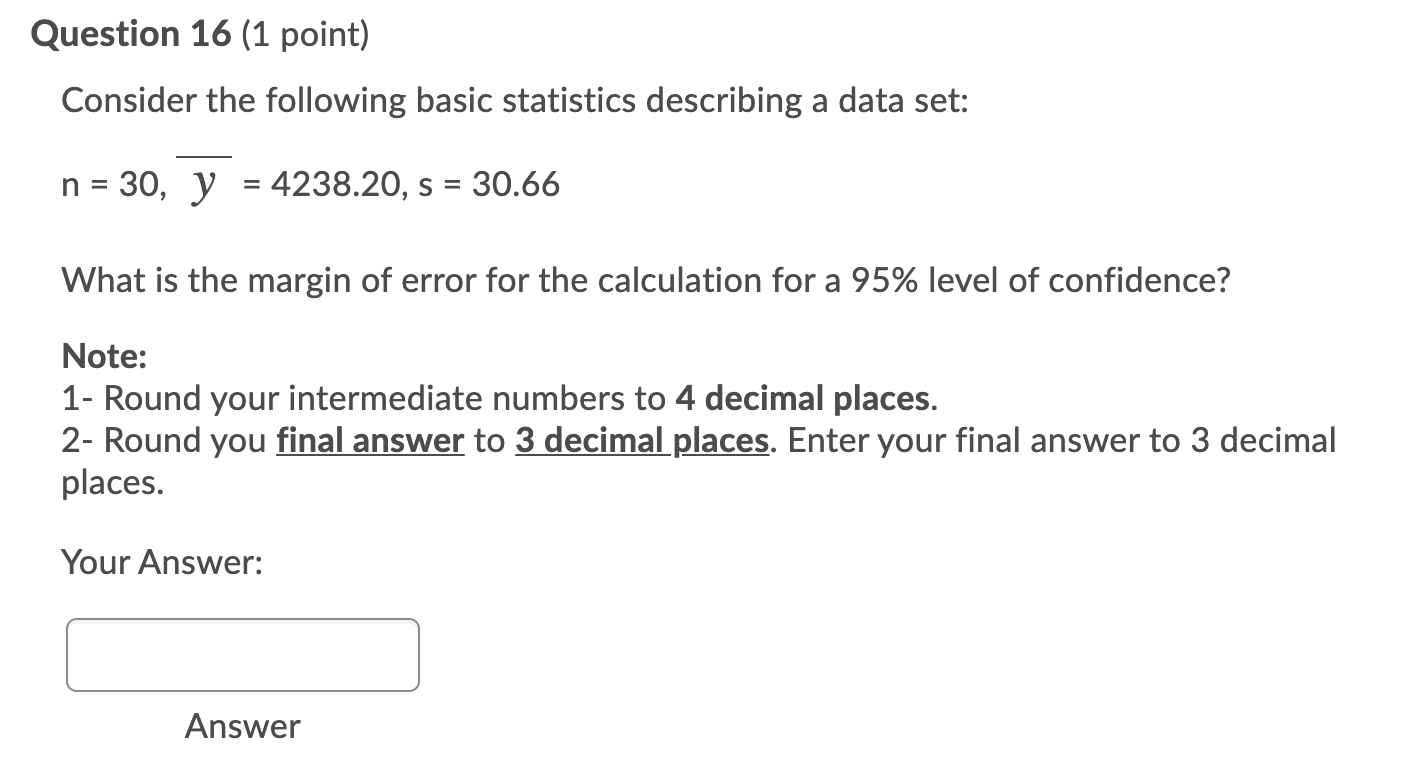



Solved Question 16 1 Point Consider The Following Basic Chegg Com
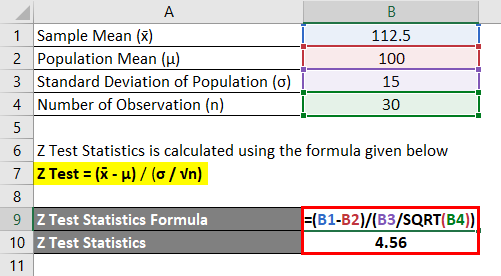



Z Test Statistics Formula Calculator Examples With Excel Template



2




For The Given Data A Find The Test Statistic B Find The Standardized Test Statistic C Homeworklib




Descriptive Statistics For Task And Test Scores N 30 Download Table




Ap Statistics Final Project A Powerpoint Presentation
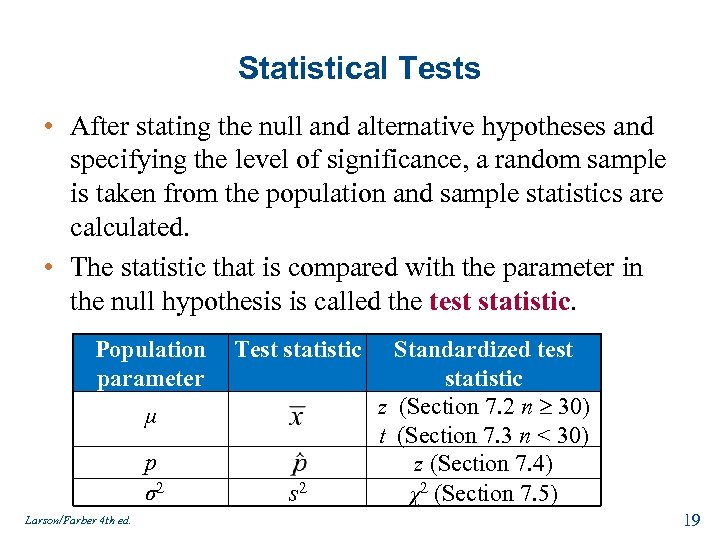



Chapter 7 Hypothesis Testing With One Sample Larson Farber




How To Test A Hypothesis For The Mean With N 30 And Sigma Known Hd Youtube



Plos One Anterior Tooth Use Behaviors Among Early Modern Humans And Neandertals




Chapter 17 Notes And Problem Set
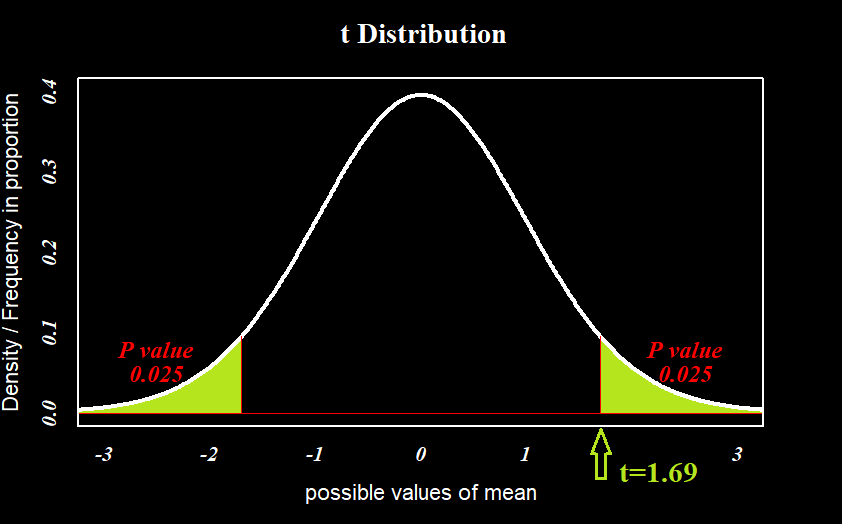



Is N 30 Really Enough A Popular Inductive Fallacy Among Data Analysts By Abhibhav Sharma Towards Data Science




Confidence Interval For A Pop Mean Using Z




Statistics Formula Sheet Coolguides




Summary Hypothesis Testing Selfengagement Assesment Null Hypothesis Song




Solution Under Which Conditions For Population Standard Deviation And Sample Size Do You Use The Formula T X




Applications Of T F And Chi2 Distributions



2
/HypothesisTestinginFinance1_2-1030333b070c450c964e82c33c937878.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples




Comparison Of Means One Sample Unknown Population Sd Env710 Statistics Review Website



Dr Arsham S Statistics Site



Solved Worksheet 1 Descriptive Statistics N 1 N 5 N 10 N 30 N 100 Statistics Variable N N Mean Se Mean Stdev Minimum Q1 Median Q3 Maximum N 1 Course Hero
.jpg)



Statext Statistical Probability Tables




Resolution Of Review Sheet Of Statistical Methods Stat 303 Docsity
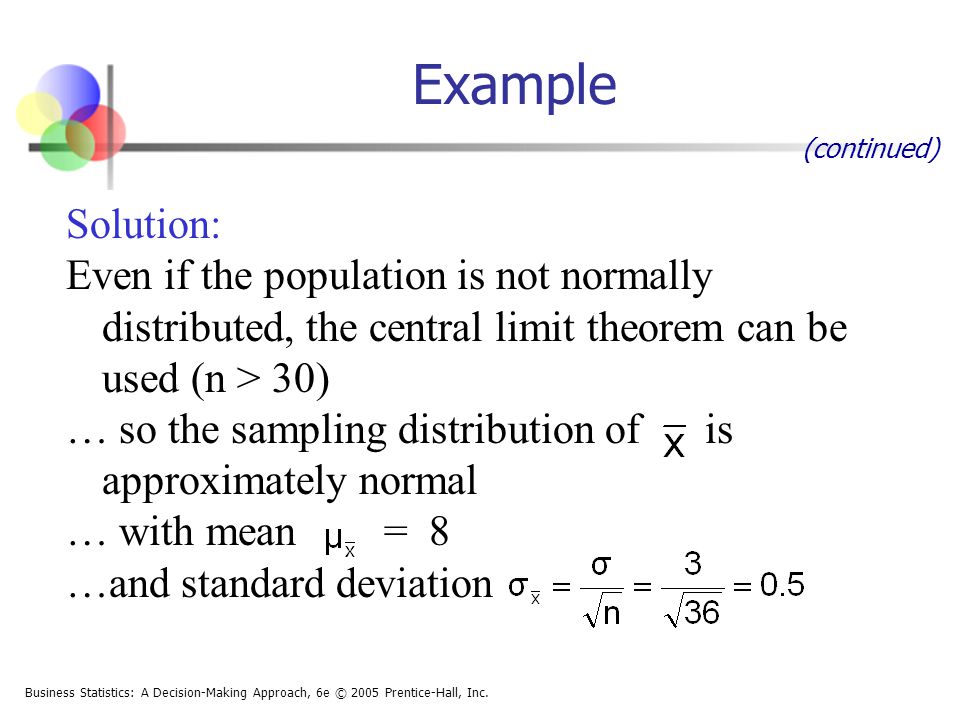



Sampling Distributions Ppt Download




Kdnuggets Kdnuggets News 18 N30 Aug 8 Iconic Data Visualisation Data Scientist Interviews Demystified Simple Statistics In Python T Co Dego5iqt63 T Co R2m50io3mh




Cross Validation Statistics Wikipedia




Njsiyxur8ldwlm
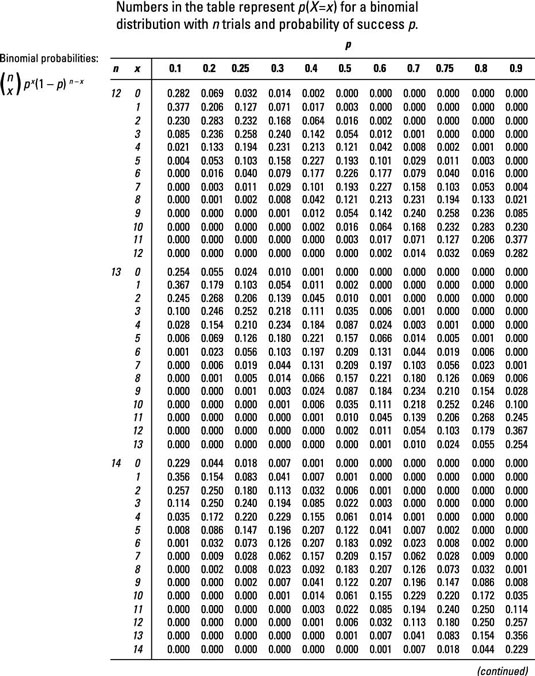



Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies




Solved Question 26 Calculate Proportion Test Statistics In Chegg Com




Solutions To Homework 8 Introduction To Statistics Stat 104 Docsity
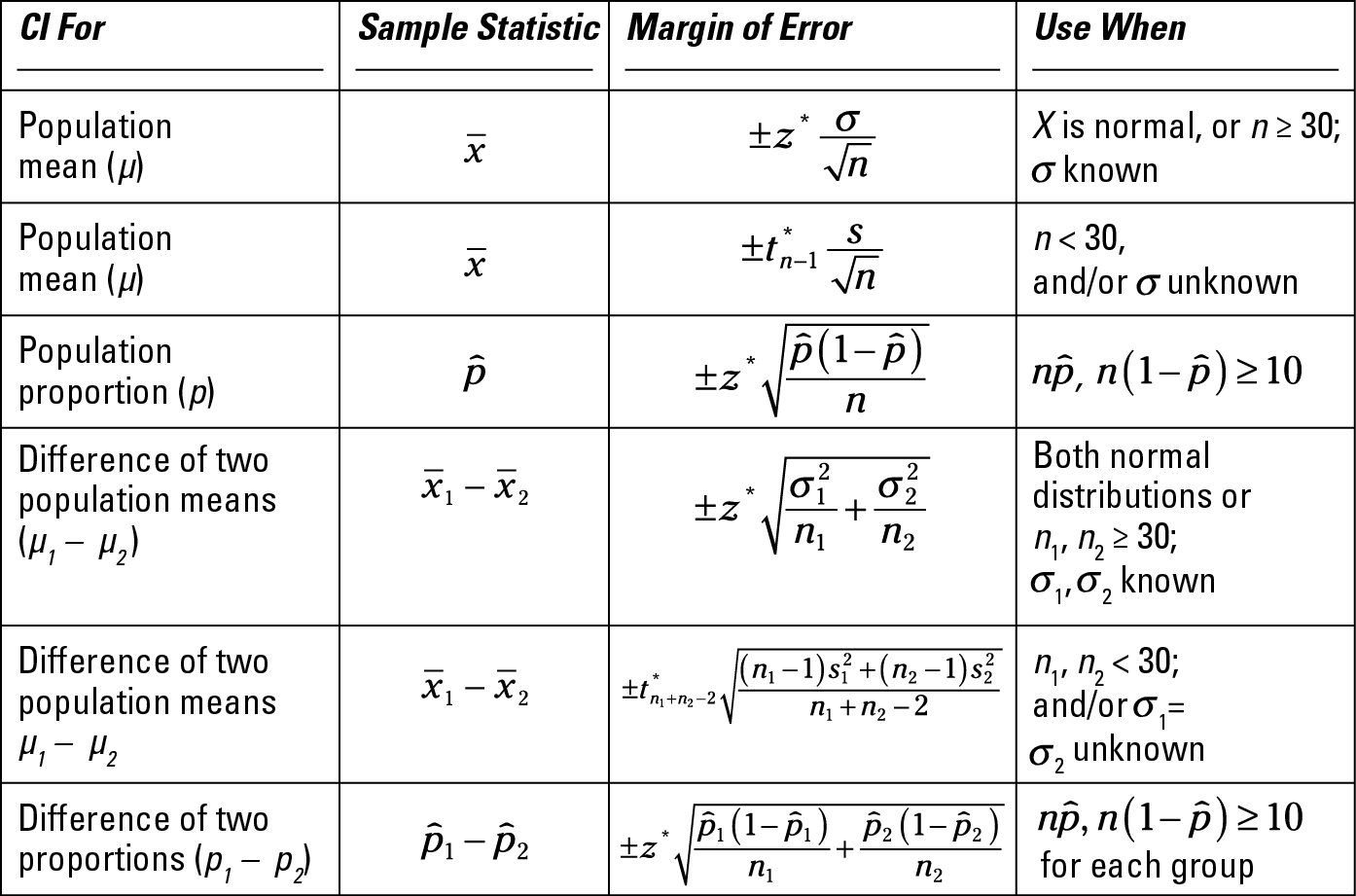



Statistics For Dummies Cheat Sheet Dummies



What Can A Small Sample Teach Us About A Big Population Part 1 By Aparna C Shastry Towards Data Science
.png)



Solved Identified And Find The Value Of The Test Statistic Refer To Table 8 Solutioninn




Calculating Test Statistics For Means And Proportions For One And Two Tailed Tests Krista King Math Online Math Tutor




Solved U Hviſ Drea At 26 Calculate Proportion Test Chegg Com




Intro To Statistics Part 9 The Central Limit Theorem L0ng C0nnect10ns




Statistics And Probability Module 4 Identifying Appropriate Test Statistics Involving Population Mean Shs Modules




Chapter 7 Introduction To Sampling Distributions Ppt Video Online Download
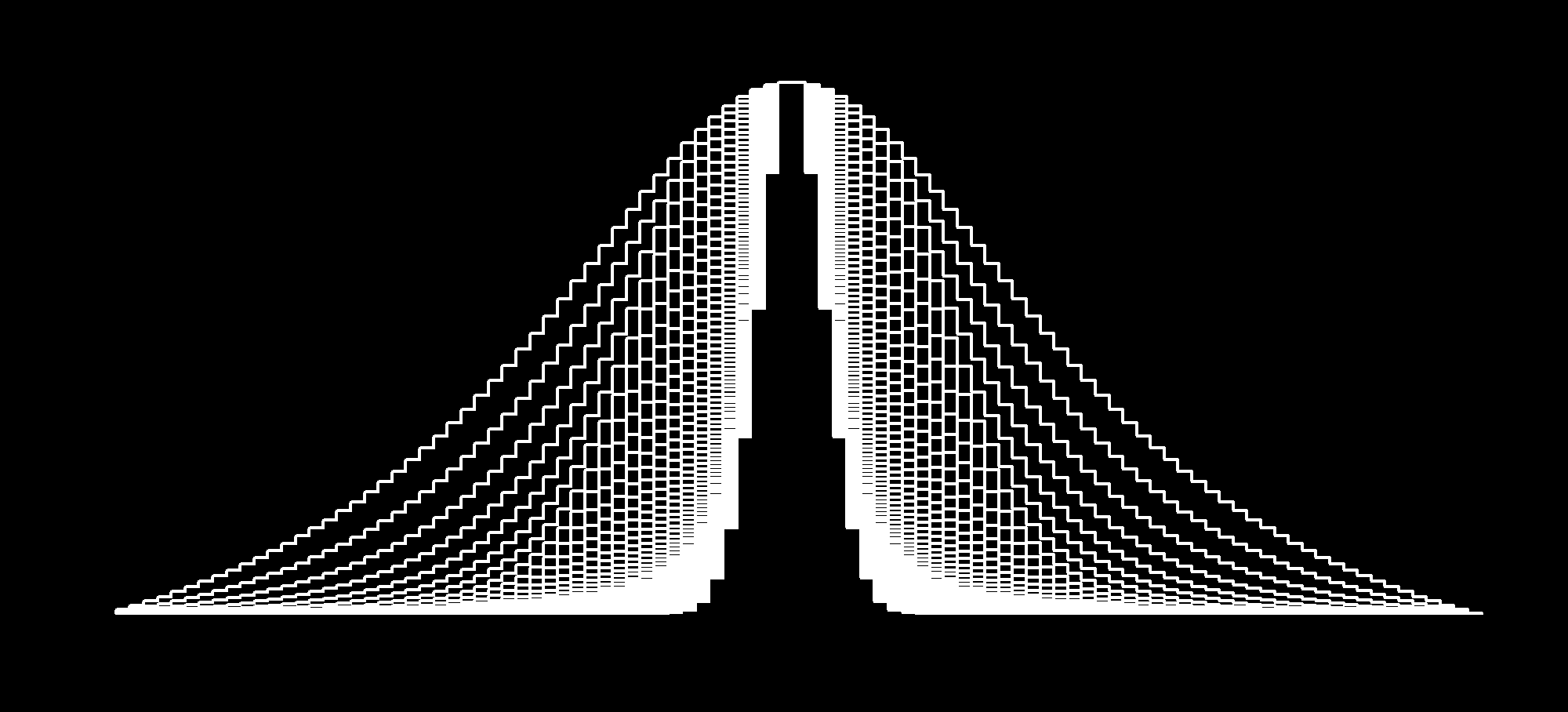



Is N 30 Really Enough A Popular Inductive Fallacy Among Data Analysts By Abhibhav Sharma Towards Data Science




1 Computing Confidence Intervals Using The Ti The Ti Can Compute An Entire Confidence Interval From Either Summary Statistics Or Data These Functions Ppt Download



What Does N Mean In Statistics Quora




Summary Of The Friedman Statistics F F K 6 N 30 And The Critical Download Scientific Diagram




Solved Which Of Tue Following In The Rejection Area Statements When The Null Would Be Applicable The Ifthe Calculated Value Of Tcsl Statistic Falls Decision Is Hypothesis Ho Is Alse A Type Correct



2



2




Data Deluge Mindless Statistics And Feynman S Conjecture



3




Ch 8 Notes Summary Statistical Techniques In Business And Economics Studocu




Stimulating Statistics Simulations News From The Nest




Baseline Characteristics Ct N 30 Bt N 32 Statistics P Value Download Table



Answers Topic 23
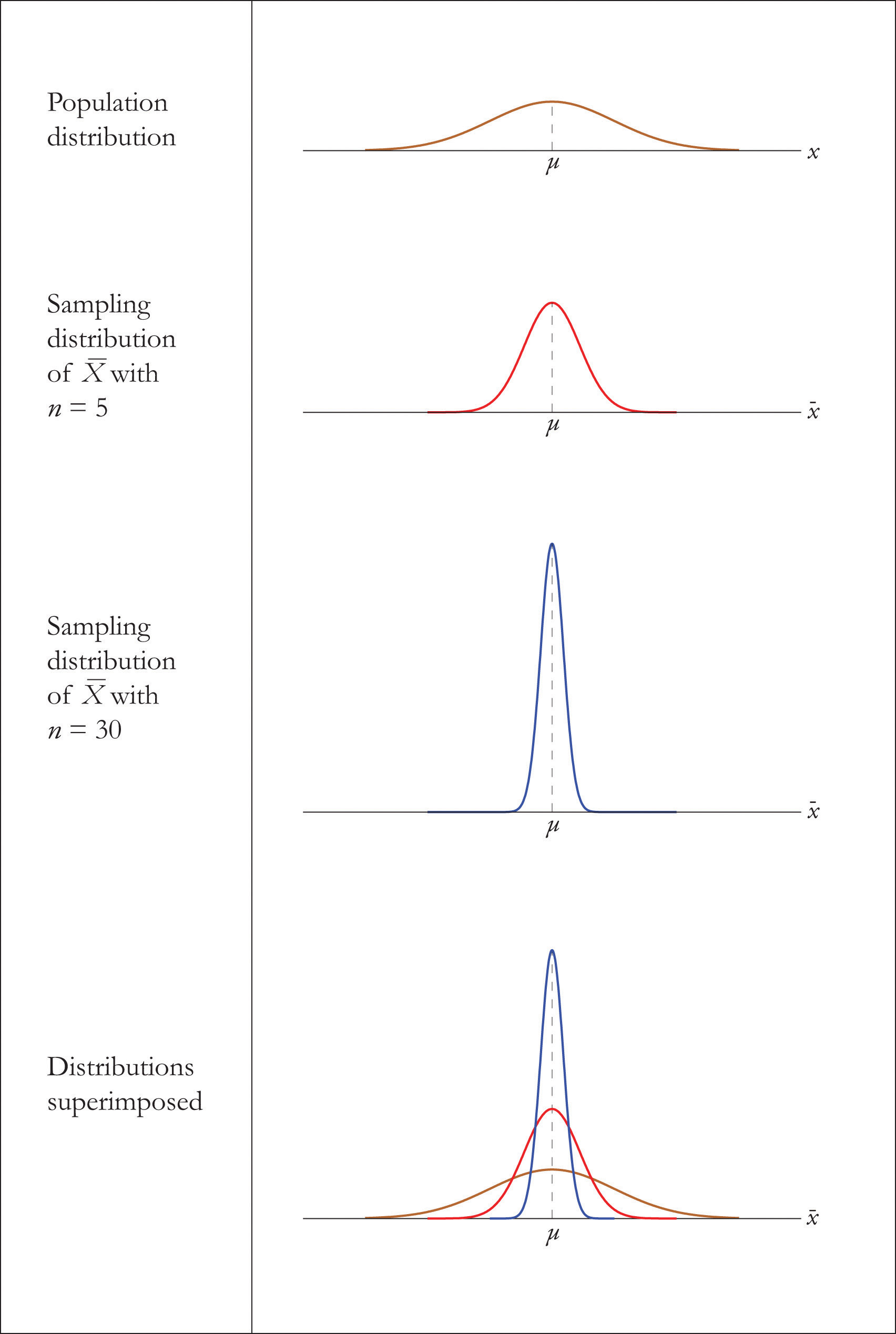



The Sampling Distribution Of The Sample Mean




Cmcp Diploma Statistics School Of Psychology University Of Nottingham 1 Overview Central Limit Theorem The Normal Distribution The Standardised Normal Ppt Download



2
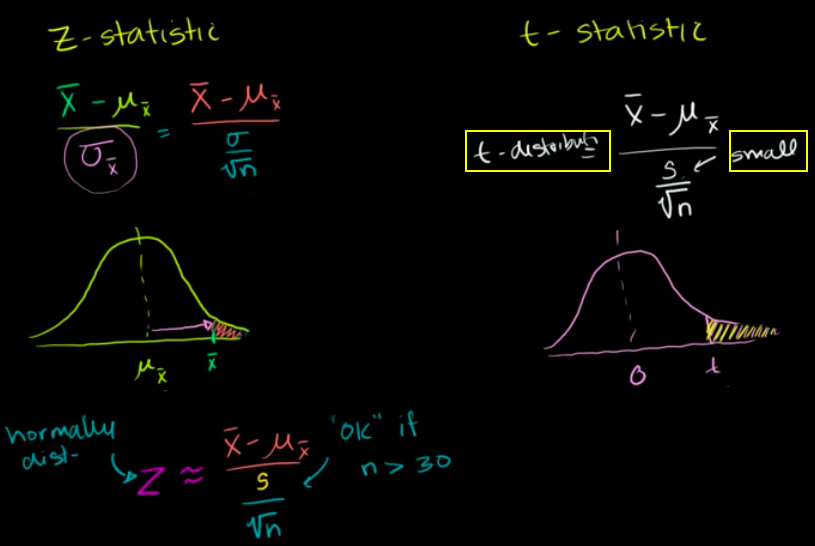



Z Test Vs T Test One Sample Refer To Khan Academy When To Use Z Or By Solomon Xie Statistical Guess Medium
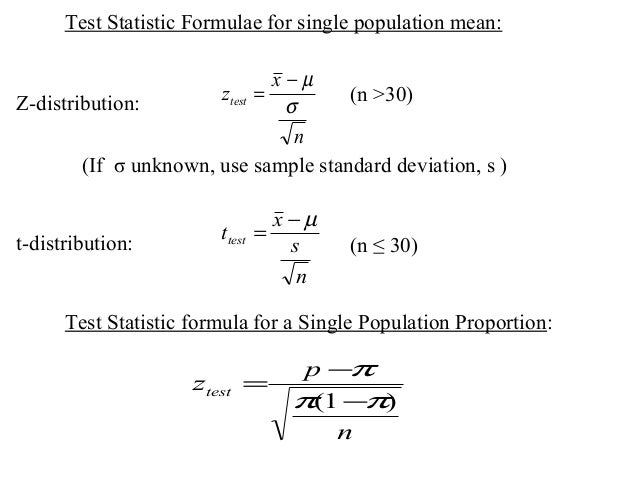



Statistics
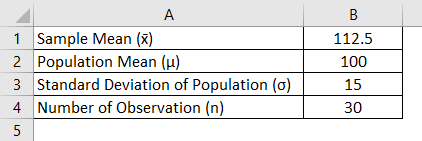



Z Test Statistics Formula Calculator Examples With Excel Template




Stats Test 3 Study Guide Stats Test 3 Study Guide Sampling Distributions Sampling Distribution Of Studocu



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿